There are few Android emulators on the Internet to test and use Andoird apps on PCs. Those are emulators, not the real Android OS like on the phone or tablet. There is a modified Android OS available that can be installed on normal 32-bit or 64-bit computers. It is called Android-x86.
This guide will show you how to install Android Oreo on VirtualBox with the pre-installed VDI image. We can avoid downloading the ISO file and installing it from scratch using the method. Also, you can use this method on Windows 11, macOS and Linux OS to have Android as a virtual machine.
Steps to Install Android on VirtualBox by VDI File
Make sure you have the latest version of VirtualBox.
1) Download the latest Android Pre-Installed VDI for VirtualBox here.
Select the VirtualBox and 32 or 64-bit version while downloading. If you are using Windows 11 or Windows 10, it will support both 64bit and 32bit platforms. Remember the version you are downloading because you need to set up the virtual machine accordingly. I used the 64bit version in this example.
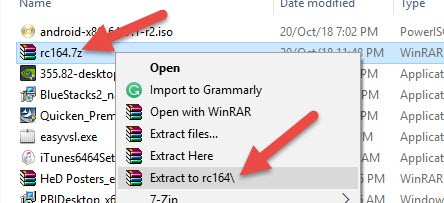
2) Extract the file. You need to have an unzipping program like 7-Zip or WinRAR for this.
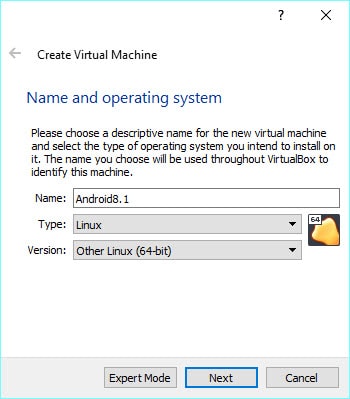
3) Create a new Virtual machine with the following configuration in VirtualBox. You can increase the settings depending on the version you install and available hardware recourse on your physical computer.
OS Type – Linux
Version – Other Linux/Linux 2.6/Oracle – Make sure to select the correct bit version, either 32 or 64, based on the file you downloaded earlier.
Memory – 512MB or more – I configured 2GB
Video Memory: 12MB or more
ACPI: Enabled
IO APCI: Enabled
PAE/NX: Enabled
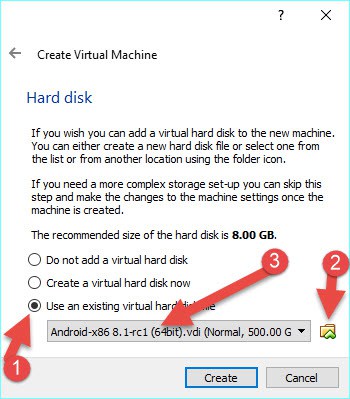
3) Select the existing disk option while setting up the virtual machine’s hard disk and browse the extracted VDI file.
See Also: How to Install Google Chrome OS on VMware
4) Start the Android virtual machine now. You will feel good seeing the OS on a larger screen than any smartphone.
Boot with the default option. It will take you to the Android OS homepage after a few seconds.
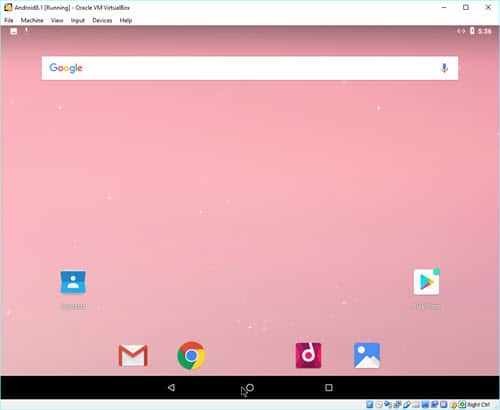
You might get stuck with the mouse/cursor movements inside the VM and unable to release it to the host Windows machine.
For better mouse integration, disable (untick) the mouse integration of the virtual machine, as shown below.
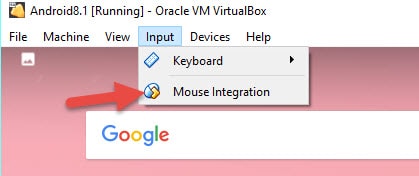
Once it is disabled, you will notice the mouse improvements inside the Android virtual machine.
Related: Message blocking is active on Android.
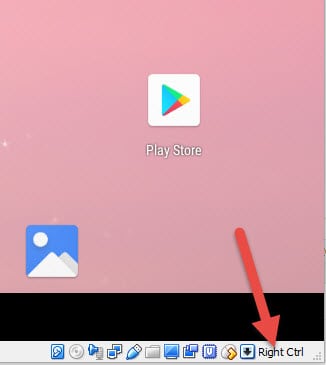
The cursor will not be released automatically to the host OS when you move the mouse outside the virtual machine. In this case, you need to manually release the cursor from the guest VM to the host computer by pressing the Right Ctrl key – you can see that option at the right bottom of the VM console.
The network and the Internet work fine inside the VM. You can set up and connect to the Play store and install Android apps in VirtualBox.

![[Solved] Mac HDMI Sound Not Working on TV While Watching a Movie](https://www.sysprobs.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/HDMI-Port-in-MacBook-211x150.jpg)

I was able to get this working and the networking is also functioning. The only thing is that it doesn’t have the Google Market app. Otherwise, it is a fully functioning Android VM. Thanks!
High!
Interesting… I have had much trouble getting network out of the VM with many operating systems (host always 64bit Linux), but it works with NAT…
With this Android tablet, however, NAT is not working. Any idea? How did you manage it to work?
Greetings,
Jagged
Okay, with PCnet-PCI II and NAT it works quite fine.
thanks!
Thanks for the information.
Thats a great news.
just got this working on ubuntu, thanks =) internet works too =)
Thanks,I have successfully run the Android on my Win 7 PC . Its works Awesome with Internet/Network…