Extending a partition (volume) in the latest Windows Operating Systems is straightforward when a computer meets the requirements. We can follow similar steps for Client and Server Operating Systems. I recently had to do the same volume extension on a Windows 2019 server running on Hyper-V, but I noticed that the extended volume greyed out in disk management. My Windows server met most of the requirements to extend a volume, but why is it greyed out?
After digging into all scenarios, I found out why I could not extend the volume even though I had an empty space on the same disk next to the partition. Though it was a Windows 2019 server in this example, the below methods are applicable for Windows 2022/2016/2012 R2 servers and client Operating Systems like Windows 10/11.
Requirements to get the ‘Extend Volume’ Option in Windows OS:
Here are the few basic requirements to get the option to extend a volume/partition when you do not have enough space.
1) The disk should have unallocated space.
There should be unallocated space on the same disk where the partition you will extend. You can’t extend a volume across different drives. If the disk doesn’t have unallocated space, then you need to delete an existing partition next to it to get unallocated space.
2) The unallocated space should be precisely next (right side) to the partition.
The extended volume will be greyed out if there is unallocated space somewhere on the same disk but not next to the partition on the right side.
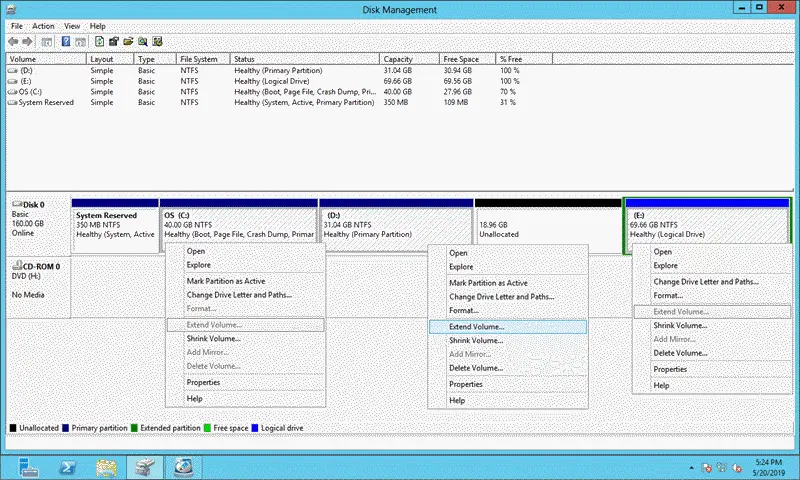
3) Only NTFS or no file system (RAW) supported
Though a partition meets the above 2 requirements, if it is formatted in FAT32 or other file systems, then you will not get the option to extend the volume.
To find out more requirements, you can check this excellent guide with screenshots and explanations.
Here is my example.
In my case, it matches all 3 requirements. My server has unallocated space on the same disk, next to the partition (on the right side), and the volume is formatted in NTFS.
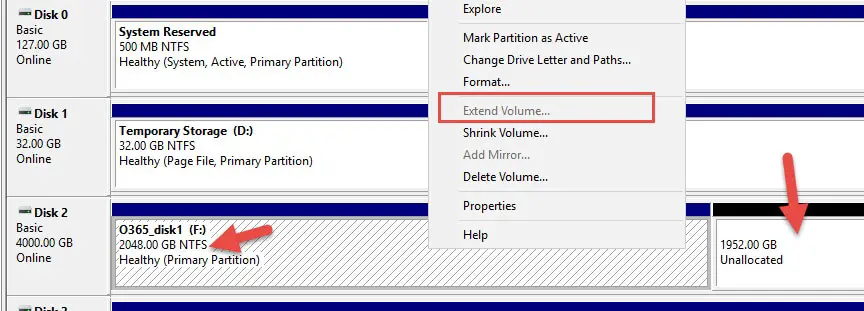
Still, Why was the Extend Volume Greyed Out?
In this example, the problem is with the size of the partition and disk format type.
The partition size is 2TB (2048GB) and is in MBR file system format.
MBR (Master Boot Record) is an old disk format that works with the legacy BIOS and all Windows Operating Systems. The maximum partition size it can have is 2TB only. Even if you create a new partition with more than 2TB on an MBR disk, it will only detect the first 2TB.
GPT is the other advanced disk format version that supports larger partition sizes. GPT has many advantages, but it can work with only the UEFI BIOS and the latest Windows Operating Systems.
Since my disk is formatted in MBR style and the partition is already 2TB, I did not get the option to extend the volume even though there is unallocated space next to it.
How to Find MBR or GPT:
To find out whether a disk is in MBR or GPT format, right-click on the disk in disk management, click Properties, and go to the Volume tab.
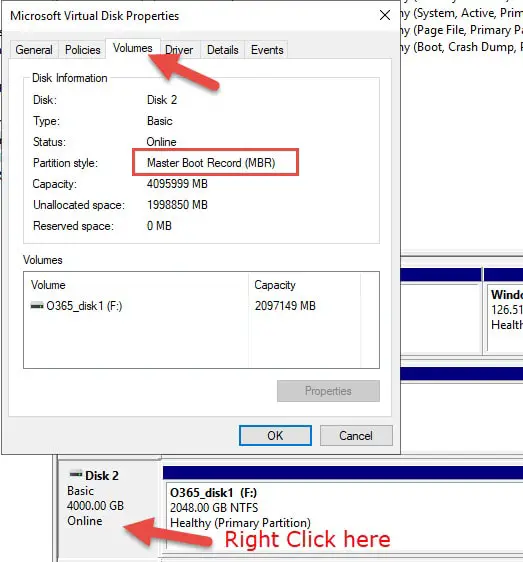
Here you will find out the style of the partition.
In summary, the extend volume option was greyed out in my case because of the MBR disk type with a 2TB partition already. In MBR disk, we can’t extend a partition for more than 2TB.
How to Extend a More than 2TB Partition on MBR Disk?
The short answer is we can’t do it. It is the limitation of the MBR disk.
The workaround would be to convert the disk from MBR to GPT if the existing Windows OS can work with GPT disks. Since most Windows clients and Server Operating Systems support GPT type, it should not be a significant concern.
-
Convert MBR to GPT without data loss.
Whatever method you try, if the data on the disk is critical, please take a backup before proceeding with any steps. Changing the disk formats, types, and file system may lead to data loss.
Few third-party disk management tools can convert a disk from MBR to GPT without data loss.
By EaseUS Disk management tool
-
MBR to GPT without any tools
We can use the same Windows disk management tool to convert a disk. But it should not have any partitions in it. In this case, we need to take a backup of the content, then delete all partitions and convert the disk.
Technically, when we delete an existing partition, then there is no need to extend it. We can create a new partition with the required size. In the future, since the disk is in the GPT file system, it can be easily extended beyond 2TB.
Also, you may not face this issue in the regular client or physical servers since the physical disk may not go beyond 2TB. But you may have larger disks and partitions in a data center environment or virtualization platforms such as Hyper-V or VMware and cloud-based solutions such as Microsoft Azure.
Next time if the extend volume is greyed out in a 2TB partition, check the disk style format, whether it is in MBR or GPT.

![[Fixed] Windows Update Stuck at 0% on Server 2016/2019/2022](https://www.sysprobs.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Downloading-update-stuck-211x150.png)

![[Solved] Change Product Key Not Working – How to Activate Windows](https://www.sysprobs.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Product-key-pop-up-did-not-work-211x150.png)
You forgot to mention formatting cluster size limitations can also cause this issue. For example windows defaults the cluster size based on the current size of the disk. In virtual environments you can increase the disk size and extend the partitions and volumes, however, if your format cluster size is small, this limits how much you can extend the volume. Example: if you format an NTFS volume with an 8k cluster size, it can only be extended to 32TB and for FAT32 it would only allow 16GB. After that you will have to transfer the data to another volume to be able to increase the size. I have had to do this a few times. https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/default-cluster-size-for-ntfs-fat-and-exfat-9772e6f1-e31a-00d7-e18f-73169155af95
Thanks – that is a good point. Since I always format in NTFS and never got a chance to extend more than 32TB 🙂